HAIR LOSS DUE TO CELIAC DISEASE
Posted by Manny Y on 7th Apr 2015
Our body needs a continuous supply of nutrients for it to function properly. Basically when we eat, the food that we ingest is broken down and absorbed through the intestines. Nutrients then travel to various tissues and organs to be utilised for energy and growth. Any excess nutrients are stored in the liver or stored as fat. In between meals or times of starvation (dieting) these stored nutrients are released back into the blood stream.
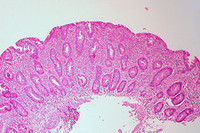
Celiac disease is a condition that causes damage to the small intestines and impairs nutrient absorption from food. Patients who have this disease cannot digest gluten, a type of protein found in wheat, barley and rye. When food containing gluten is ingested, the immune system of these patients somehow attacks and destroys the lining of the small intestine, more specifically the villi. These microscopic finger-like protrusions are found all over the small intestines and are responsible for nutrient absorption. If the whole intestinal lining is damaged, then nutrients cannot be absorbed and this can cause malnutrition.
Common signs and symptoms of celiac disease are:
* Easy fatigability
* Iron deficiency
* Osteoporosis
* Infertility
* Arthritis
* Hair loss
Patients with celiac disease may or may not exhibit any symptoms. For people who have signs of hair loss, a topical hair loss treatmentcan help increase and stimulate hair growth. The best management for this condition is to avoid any food containing gluten.

